Asking questions about what you can and can’t do after receiving dental implants is a valuable and important part of preparing for your treatment. This is because the answers you are given can let you know what steps you need to take to make a smooth recovery and get the best result from your procedure. One of the most common questions that we are asked is what happens when smoking after dental implant surgery.
While physically there is nothing to stop you from smoking after dental implant surgery, we cannot advise against it strongly enough. We all know that smoking is bad for our health and well-being. However, if there is one habit that could severely compromise your dental implants it would be smoking.
Don’t let tooth loss hold you back! Call PGA Dentistry at 561-627-8666 to restore your smile in North Palm Beach, Jupiter, and West Palm Beach! Our Palm Beach Gardens dentist provides clear instructions to help you care for dental implants.
Why Is Smoking Bad News for Dental Implants?
Smoking Increases Your Risk of Gum Disease
 By far the biggest threat to dental implants from smoking comes in the form of gum disease. Gum disease is a condition that is characterized by an infection in the soft tissue of the gums. This infection stems from bacterial growth in the dental plaque that forms in the pockets around your teeth when you fail to brush them properly. If plaque dries and hardens because it hasn’t been effectively removed, it forms something called tartar.
By far the biggest threat to dental implants from smoking comes in the form of gum disease. Gum disease is a condition that is characterized by an infection in the soft tissue of the gums. This infection stems from bacterial growth in the dental plaque that forms in the pockets around your teeth when you fail to brush them properly. If plaque dries and hardens because it hasn’t been effectively removed, it forms something called tartar.
Studies have shown that smokers have far more tartar on their teeth than those people who do not smoke, and one of the main reasons for this is believed to be the decreased production of saliva that they experience. Saliva is our body’s natural defense against dental decay since it helps to wash away food particles and bacteria. This decrease occurs due to damage to the salivary glands caused by smoking.
If left untreated, gum disease can affect the bone structure that supports your teeth. However, if you have dental implants and the structure of your jawbone is compromised, it could cause the implant posts that are holding your prosthetic teeth in place to come loose and potentially fall out.
Some studies have shown that smokers see a greater rate of bone deterioration than non-smokers, as much as 0.16mm (about 0.01 in) per year. While this may not sound a great deal, over the course of several years, it could reduce the lifespan of your dental implants.
Smoking Affects Your Ability to Heal
Another key problem with smoking after dental implants, particularly if you light up within hours or even days of your surgery, is that smoking actually inhibits the healing process. This is due to the chemicals contained within nicotine interfering with the flow of oxygenated blood to the gums, which is essential if the cells are to repair and heal themselves.
Dental implants are reliant on the jawbone and gum tissue healing around them to secure them permanently in place – a process known as osseointegration. If this healing process is compromised, it could drastically affect the success of the procedure.
The initial few weeks following surgery are the most crucial as this is when osseointegration starts. Smoking during this time can significantly increase the chance of infection or lead to implant failure, the latter of which can render the entire surgery a waste of time.
How Long Should I Give Up Smoking?
If you only intend on giving up smoking for the minimum possible duration, you should be aware that you are putting the longevity of your dental implants at risk. However, if you do not intend on giving up forever, we strongly recommend that you stop smoking at least a week before your dental implant surgery, and for at least two to three weeks after.
While everyone should follow a robust oral healthcare routine, it is especially important for smokers as it can help reduce your risk of suffering from periodontal disease.
Smoking and Dental Implants
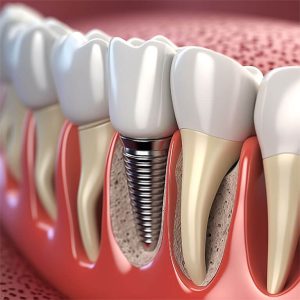
Dental implant surgery is a common and effective way to replace missing teeth. The procedure involves the placement of a metal post into the mouth, which acts as an anchor for a replacement tooth.
While dental implant surgery has a high success rate, it requires careful post-operative care to ensure proper healing and long-term success. Smoking is one of the most significant factors that can affect the success of dental implant surgery.
Effects of Smoking on Dental Implant Surgery
Smoking can significantly impact the healing process after dental implant surgery. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow and oxygen supply to the surgical site. This can slow down the healing process and increase the risk of infection. Smoking can also weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight infections.
Risks of Smoking After Dental Implant Surgery
Smoking after dental implant surgery can increase the risk of implant failure. The heat from smoking can cause the metal post to expand and contract, weakening the bone around the implant and causing it to fail. Smoking can also increase the risk of gum disease, leading to implant failure.
Consequences of Smoking on the Success of Dental Implant Surgery
The consequences of smoking after dental implant surgery can be severe. Implant failure can result in the need for additional surgeries, which can be painful and costly. Smoking can cause other oral health problems, such as gum disease and oral cancer. Additionally, smoking can hurt overall health, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, gum disease, and other health problems.
Importance of Smoking Cessation
Quitting is one of the best things you can do for your oral health. Quitting smoking before and after dental implant surgery is important to ensure the best possible outcome. Quitting smoking can improve blood flow and oxygen supply to the surgical site, promoting healing and reducing the risk of infection. It can also improve overall health and reduce the risk of other health problems.
Techniques and Resources for Quitting Smoking
There are many techniques and resources available to help people quit smoking. Nicotine replacement therapy, such as gum or patches, can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Behavioral therapy and support groups can provide encouragement and support throughout the quitting process. Your dentist or doctor can also provide guidance and support.
Quitting smoking is essential for the success of dental implant surgery and overall health. If you are a smoker and considering dental implant surgery, quitting smoking before and after the procedure is essential to ensure the best possible outcome. With the help of your dentist or doctor, and the many resources available, you can quit smoking and achieve better oral and overall health.
Smoking and Gum Health: Understanding the Link and Its Consequences
Smoking is prevalent worldwide, with millions of people using tobacco products regularly. While most people know the harmful effects of smoking on their lung health, it is also essential to understand its impact on gum health. Smoking is a significant risk factor for oral health problems, affecting the gums and bones supporting the teeth. This article will discuss the link between smoking and gum health, its mechanisms, and its consequences.
Smoking and Gum Disease
Gum disease is a common condition ranging from a mild inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) to severe infection and bone loss (periodontitis). Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum problems, with smokers being up to six times more likely to develop it than non-smokers. Furthermore, smoking can make gum disease more severe and harder to treat.
Mechanisms of Smoking’s Effects on Gum Health
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause significant damage to oral tissues. Smoking reduces blood flow and oxygen supply to the gums, making them more vulnerable to infection and inflammation. Smoking also weakens the body, making it harder for the immune system to fight infections. As a result, smokers are more likely to develop gum disease, and the condition can be more severe and harder to treat.
Consequences of Gum Disease Caused by Smoking
The consequences of gum disease caused by smoking can be severe. Smokers are more likely to experience tooth loss, receding gums, and bone loss. Additionally, smoking can cause other oral health problems, such as bad breath, stained teeth, and oral cancer. Furthermore, gum disease caused by smoking can increase the risk of health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, and respiratory infections.
Prevention and Treatment of Gum Disease Caused by Smoking
The most effective way to prevent gum disease caused by smoking is to quit smoking. Quitting smoking can improve blood flow and oxygen supply to the gums, making them healthier and more resistant to infection. It can also improve overall health and reduce the risk of other health problems.
In addition to quitting smoking, regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for preventing and treating gum disease. Your dentist can assess your oral health and recommend treatment options if necessary. Professional gum disease treatment options may include scaling and root planning, gum surgery, or antibiotics. At-home oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, can also help prevent gum disease.
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease, severely affecting oral health and overall well-being. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage oral tissues, reduce blood flow and oxygen supply to the gums, and weaken the immune system.
Quitting smoking, regular dental check-ups and cleanings, and professional gum disease treatment options with our Palm Beach Gardens dentist are essential for preventing and treating gum disease caused by smoking. By understanding the link between smoking and gum health, you can make informed decisions to protect your oral and overall health.
Other Effects of Smoking on Your Oral Health
How Smoking Causes Tooth Stains
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause significant damage to teeth. Smoking can cause tooth stains by leaving behind a sticky residue of nicotine and tar on teeth, which can easily absorb pigments from food and drinks. Over time, these stains can become more difficult to remove, leading to yellow, brown, or gray discoloration of the teeth.
Types of Tooth Stains Caused by Smoking
There are two types of tooth stains caused by smoking: surface and intrinsic. Surface stains are stains on the surface of the teeth caused by external factors, such as tobacco use, food, and drinks.
Intrinsic stains develop inside the tooth, caused by changes in the tooth’s structure, such as tobacco use. Smoking can also cause other discolorations, such as a black hairy tongue, caused by an overgrowth of bacteria in the mouth.
Consequences of Tooth Stains Caused by Smoking
The consequences of tooth stains caused by smoking can be severe. Tooth discoloration can negatively impact your appearance and make you feel self-conscious. The bacteria that cause tooth stains can also cause bad breath and other health problems. Finally, tooth discoloration caused by smoking can also have psychological effects, such as making you feel less confident in your smile.
Need Information About Smoking After Dental Implant Surgery?
For more information on smoking and dental implant procedures, or to schedule a consultation to discuss dental implant surgery in Palm Beach Gardens, FL, call PGA Dentistry today at 561-627-8666. Serving North Palm Beach, Juno Beach, and Singer Island!

